How to move from Financial Controller to Finance Director

Transitioning from Financial Controller to Finance Director requires strategic fluency in capital allocation, governance, and valuation. Learn what differentiates candidates.
AI in Finance: When Knowledge Is Automated, What Creates Value?
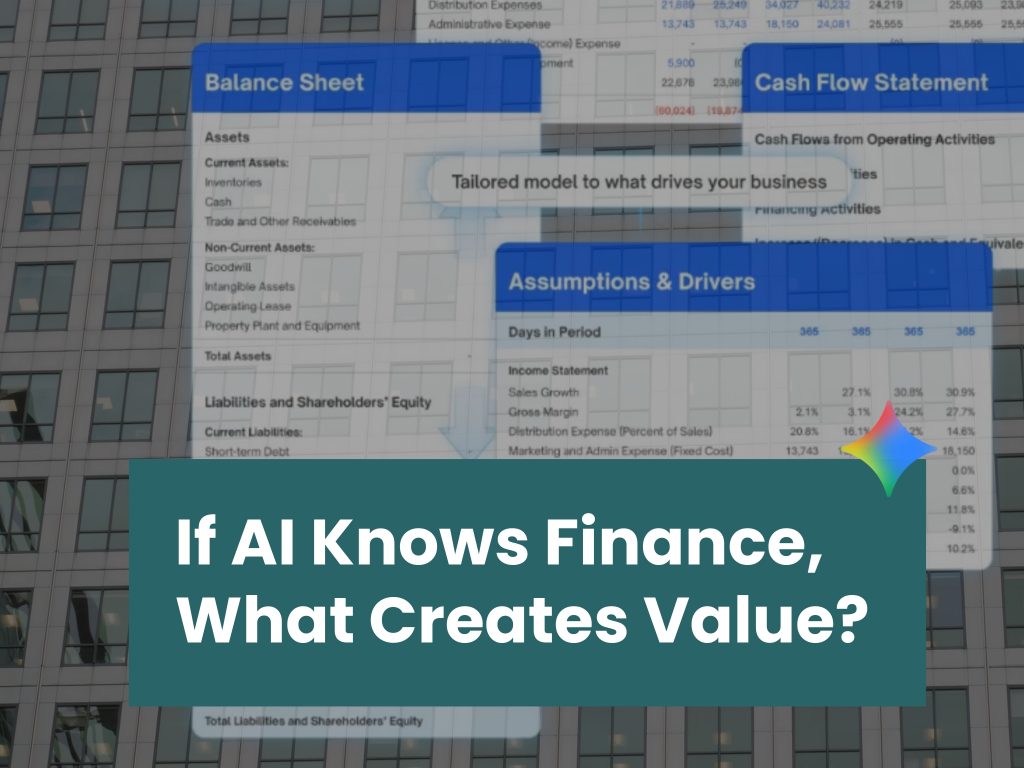
AI can now build financial models and automate analysis. The real value in finance lies in judgement, oversight, and capital discipline.
How Investment Decisions Are Evaluated in Practice

How investment decisions are evaluated in practice, beyond NPV and IRR, including judgement, risk, and capital allocation trade-offs.
Metrics, KPIs and OKRs: The Pyramid Framework Explained
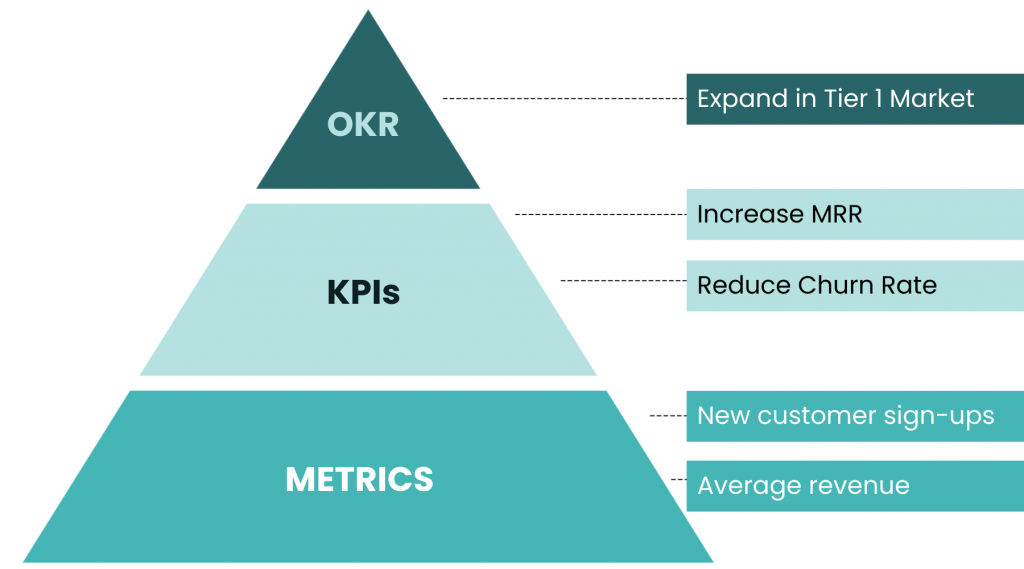
A clear executive explanation of how metrics become KPIs, and KPIs become OKRs, using a practical pyramid framework for reporting and strategy.
Beyond the Hype: Generative AI Explained for Finance & Governance
Generative AI is reshaping finance, strategy, and governance. Learn what it actually does, where it adds value, and where leaders should remain cautious.
SaaS Valuation Metrics: EBITDA, Revenue & EV Multiples
How EBITDA, revenue, and enterprise value multiples are used to value SaaS companies, illustrated through public comps, transactions, and DCF analysis.
What Is a Provision in Accounting? | Accounting Series | CLFI
An overview of what a provision is in accounting, how it is recognised and measured, and how it differs from contingent liabilities.
Levered Free Cash Flow (LFCF)? Definition and Formula

Levered Free Cash Flow (LFCF) shows the cash available to shareholders after debt payments. Learn its definition, formula, and use in equity valuation.
What Is Unlevered Free Cash Flow (UFCF)? Definition and Formula

Unlevered Free Cash Flow (UFCF) measures cash generated by a business before financing decisions. Learn its definition, formula, and role in valuation.
Current Ratio and Quick Ratio Explained (Liquidity Analysis)
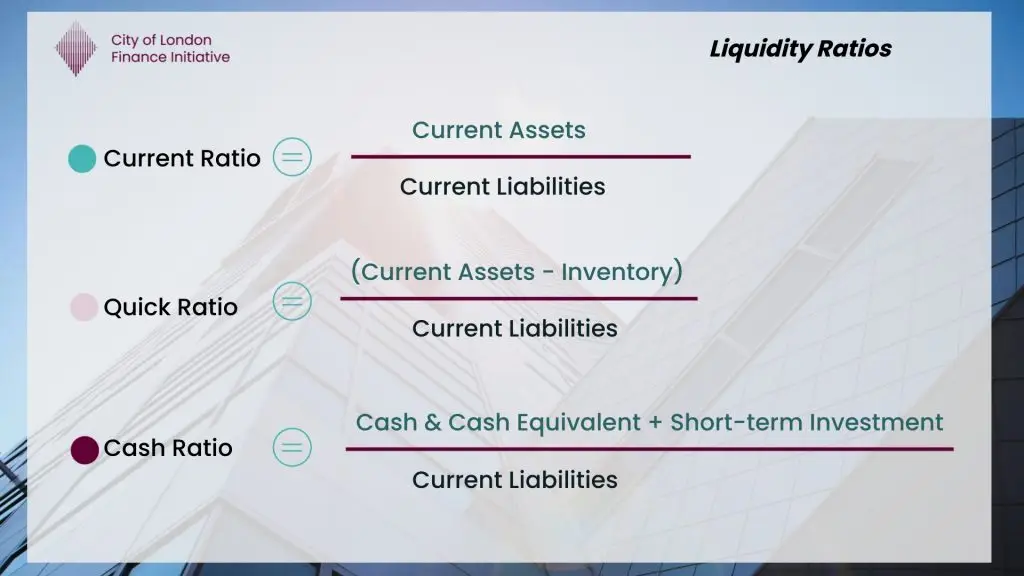
Understand the current ratio and quick ratio, how they measure liquidity, and how boards use them to assess short-term financial resilience.
